Polycythaemia vera resources
Don’t miss out on these resources to support you and your patients.
This page is intended for UK healthcare professionals and other relevant decision makers only. If you are a member of the public, please click here.
This portal is funded and owned by Novartis Pharmaceuticals UK Ltd and includes content approved by Novartis.
Adverse events reporting information can be found in the footer of this page.
The British Society for Haematology recommends a variety of first-, second- and third-line treatments for patients with PV.1 Click here to see the BSH guideline recommendations.
Patients can become intolerant or resistant to conventional therapies2
HU is often used as a first-line cytoreductive treatment in high-risk patients.2 For patients under the age of 60, interferon* can be recommended instead.1,3,4
Switching to a second-line treatment may need to be considered, depending on individual patient factors.4 Up to 20.7% of patients with PV may become intolerant or resistant to HU treatment, which may lead to increased mortality.†5–7
Use the modified ELN recommendations to identify intolerance and resistance.4
*Not all forms of interferon therapies are licensed for the treatment of PV. Please refer to individual summary of product characteristics prior to prescribing.
Intolerance
Haematologic toxicities
Absolute neutrophil count <1.0 × 109/L
Platelet count <100 × 109/L
Haemoglobin <10 g/dL
Non-haematological toxicities
Fever
Manifestations of the mucous membrane
Gastrointestinal symptoms
Pneumonitis
Leg ulcers
Resistance
Thrombosis or bleeding
Unacceptable number of phlebotomies to keep HCT <45%‡
Persisting disease-related symptoms
Platelet count >400 × 109/L and/or white blood cell count >10 × 109/L‡
No reduction of splenomegaly or a reduction <50%‡
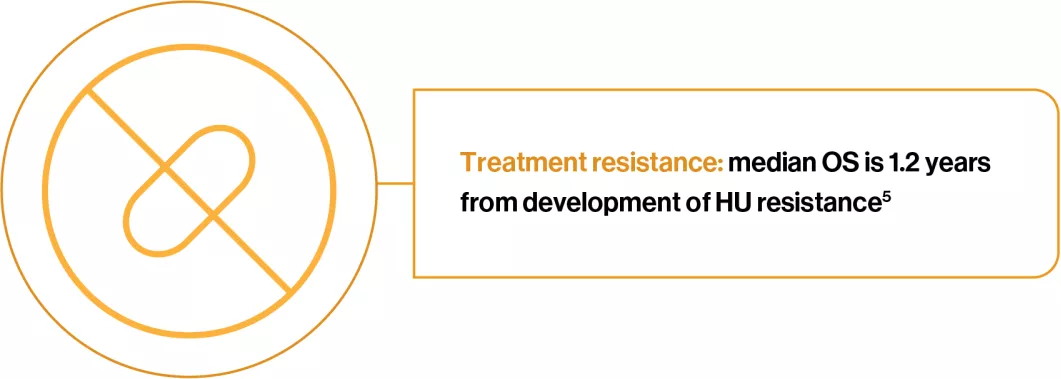
The development of HU resistance, as defined by the ELN criteria, was assessed in patients with PV that were treated with HU for a median time of 4.4 years (n=261). Patients that developed HU resistance, compared to those that did not, experienced a:5
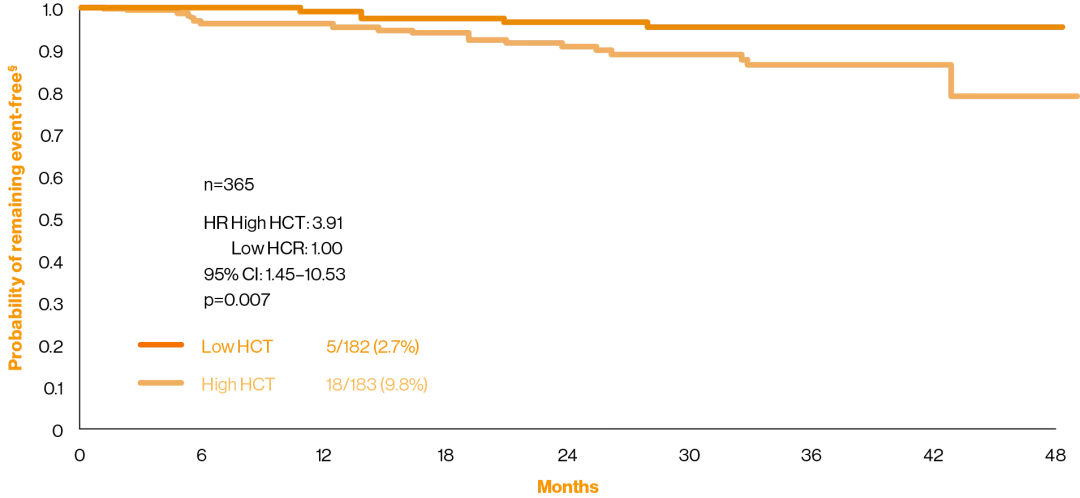
The CYTO-PV study was a large-scale, multicentre, prospective, randomised clinical trial comparing the efficacy of phlebotomy, HU or both for maintaining a HCT target of less than 45%, as compared with maintaining a target of 45–50%, for the prevention of thrombotic events in patients with polycythaemia vera (n=365). The protocol dictated that the HCT target to which patients were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio had to be maintained during the course of the study. The primary composite endpoint was the time until death from cardiovascular causes or major thrombotic events.§8
Adapted from Marchioli, et al. 2013.8
In a prospective, non-interventional study of skin alterations in 151 patients with MPNs (n=55 with PV) who gave informed consent:9
Patients with PV are recommended to switch to a second-line cytoreductive therapy if they meet the criteria for intolerance or resistance.3 The 2021 ELN recommendations for treatment suggest that treatment choice should be based on individual clinical features:3
Age
Spleen size
Symptoms
History of skin cancers
Patient preference
Hydroxyurea is synonymous with/refers to hydroxycarbamide throughout.
†HU resistance or intolerance was defined using the 2010 ELN criteria.7,11 In a retrospective analysis of 106 patients with PV in Belgium, when using the original and modified ELN criteria, 20.7% and 39.6% of patients were resistant or intolerant to HU, respectively.4,7,11
‡After 3 months of at least 2 g per day of HU or the maximum tolerated dose.5
§Event is defined as death from cardiovascular causes or thrombotic events (stroke, acute coronary syndrome, transient ischaemic attack, pulmonary embolism, abdominal thrombosis, deep-vein thrombosis, or peripheral arterial thrombosis).8
BSH, British Society for Haematology; CI, confidence interval; CV, cardiovascular; ELN, European LeukemiaNet; HCT, haematocrit; HR, hazard ratio; HU, hydroxyurea; IFN-alpha, interferon-alpha; MPN, myeloproliferative neoplasms; OS, overall survival; PV, polycythaemia vera; QoL, quality of life.
References
McMullin F, et al. Br J Haematol 2019;184:176–191.
Raman I, et al. Leuk Lymphoma 2021;62:2310–2319.
Marchetti M, et al. Lancet Haematol 2022;9:e301–e311.
McMullin F, et al. Br J Haematol 2016;172:337–349.
Alvarez-Larrán A, et al. Blood 2012;119:1363–1369.
Alvarez-Larrán A, et al. Br J Haematol 2016;172:786–793.
Demuynck T, et al. Ann Hematol 2019;98:1421–1426.
Marchioli R, et al. N Engl J Med 2013;368:22–33.
Stegelmann FA, et al. EHA Congress 2017, 22–25 June; Madrid, Spain. Abstract E1335.
Harrison CN, et al. Ann Hematol 2017;96:1653–1655.
Barosi G, et al. Br J Haematol 2010;148:961–963.
UK | February 2025 | FA-11213873
Adverse events should be reported. Reporting forms and information can be found at www.mhra.gov.uk/yellowcard.