

Complement-mediated diseases
The complement system
The complement system is part of the immune system, consisting of over 30 different activating and inhibiting proteins, regulators and receptors, working sequentially and collaboratively to clear toxic materials and defend against infection.1,2
When functioning correctly, the complement system leads to the destruction of foreign or damaged cells, while ensuring the destruction stops once the threat is removed before causing damage to healthy cells and tissue.3
The complement system works as a sequence, running in three separate activation pathways that ultimately converge into a common cell-killing pathway.2 Depending on the activators involved, the system follows either the:1,2
Classical pathway (antibody-triggered)
Lectin pathway (bacterial sugar-triggered)
Alternative pathway (antibody-independent activation)
Watch the animation below to learn more about the three pathways that make up the complement system.
Watch the animation below to learn more about the three pathways that make up the complement system.
Introduction to the complement system
Watch the video below to hear Professor Paul Morgan and Professor David Kavanagh discuss the complement system and the diseases that are associated with its overactivation.
A conversation on the complement system and complement-mediated diseases
Watch the video below to hear Professor David Kavanagh discuss how the complement system is involved in specific kidney diseases.
Understanding complement-mediated kidney disease
Watch the animation below to learn about the complement system and the three main pathways involved.
Complement cascade
The diagram below shows the proteins involved in the complement pathways and illustrates their convergence into one:1,2
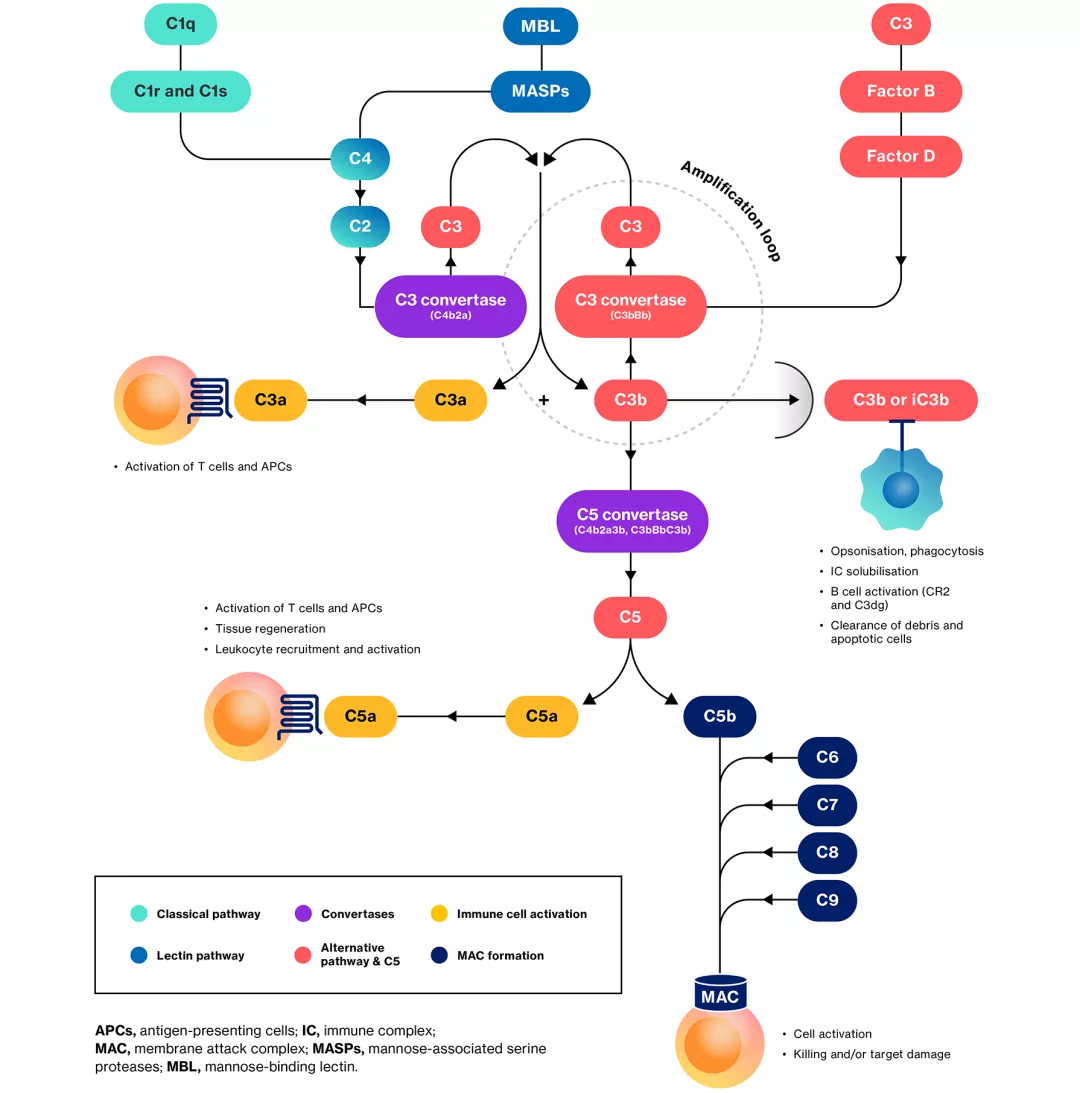
Adapted from Morgan BP & Harris CL, 2015.2
Activation of the complement system is tightly regulated by a series of soluble and membrane-bound proteins. Internal or external factors can disrupt the function of these proteins, causing dysregulation. Dysregulation can lead to the complement system mistakenly destroying healthy cells and tissue, causing a variety of complement-mediated diseases.3,4
Complement-mediated diseases
Defects at different stages of the complement system lead to various clinical outcomes. For example, defects in the early components of the classical pathway increase the risk of autoimmune disease, and problems in the terminal pathways are associated with susceptibility to infections.1,2
Complement-mediated diseases can fall into several categories. An incomplete list is shown below.2,5–10 For more information on the specific diseases, please follow the links where given .
Process | Disease examples |
Acute injuries | Haemodialysis |
Autoimmune | Antiphospholipid syndrome |
Degenerative | Dementia |
Haematological | Hereditary angioedema |
Inflammatory | Anaphylaxis |
Ischaemia-reperfusion | Myocardial infarction |
Renal | Atypical haemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) |
Complement dysfunction has also been linked to other conditions, including cancer, allergic asthma, transplant rejection and periodontitis.5
Download our infographic that outlines the conditions caused by dysfunctions of different proteins within the complement system.
AAV, ANCA-associated vasculitis; aHUS, atypical haemolytic uremic syndrome; ANCA, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; ARDS, sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; HUS, haemolytic uremic syndrome; IgA, imunoglobulin A; MPGN, membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis; PNH, paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria; TTP, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
References
Medscape. Complement Related Disorders. Available at: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/135478-overview [Accessed September 2025].
Morgan BP & Harris CL. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2015;14(12):857–877.
Noris M & Remuzzi G. Semin Nephrol 2013;33(6):479–492.
Fukuzawa T, et al. Sci Rep 2017;7(1):1080.
Ricklin D, et al. Nat Immunol 2010;11(9):785–797.
Novartis. Complement-mediated kidney diseases and their impact. Available at: https://www.novartis.com/patients-and-caregivers/diseases/kidney-disease/complement-mediated-kidney-diseases-and-their-impact [Accessed September 2025].
Smith R, et al. Nat Rev Nephrol 2019;15:129–143.
Schena F, et al. Int J Mol Sci 2020;21:525.
Wong EKS, et al. Semin Immunopathol 2018;40(1):49–64.
Boyd J, et al. Kidney Int 2012;81:833–843.
UK | September 2025 | FA-11496801
Adverse events should be reported. Reporting forms and information can be found at www.mhra.gov.uk/yellowcard.





