
Early diagnosis of AxSpA is critical because patients with early-stage disease are estimated to have at least the same level of disease activity and pain as patients in the later stages.2

Stiffness
90.2%.3

Pain
In 83.1% of AS patients.3
Fatigue
In up to 80% of AS This symptom represents a persistent, unmanageable, and unpredictable issue.4
Night back pain
75% of AS patients awakened at night due to back pain.5
Early and maintained effect to give patients control over their lives6
Improvement was seen as early as week 1 and sustained through week 52.6
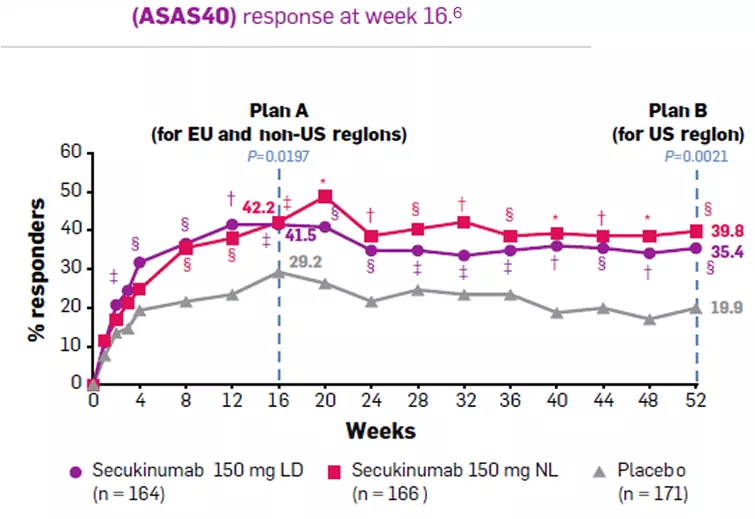
ASAS40 response in TNFi-naive patients was significantly higher in the Cosentyx 150 mg LD group (41.5%) compared with the placebo group (29.2%) at week 16 (P = 0.0197) and significantly higher in the Cosentyx 150 mg NL group (39.8%) compared with the placebo group (19.9%) at week 52 (P = 0.0021).6 |
Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society criteria for 40% improvement (ASAS40) response at week 16 (analysis plan A for European Union [EU] and non-US region regulatory requirements) and week 52 (analysis plan B for US regulatory requirements) in tumor necrosis factor inhibitor–naive patients randomized to receive Cosentyx 150 mg with loading (LD), Cosentyx 150 mg without loading (NL), or placebo (primary objective).6
Prevent study design
Objective: PREVENT is the first phase III study evaluating the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of secukinumab 150 mg, with or without loading doses, in patients with active nonradiographic axial SpA. Here, we report the efficacy up to week 52 and the safety results for the entire treatment period (including at least 52 weeks of exposure for all patients and up to 104 weeks of exposure for some patients) from the PREVENT study.6
Study Design: PREVENT is an ongoing randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled 2-year phase III study with an extension of up to 2 years in patients with nonradiographic axial SpA. 1583 patients were randomized (1:1:1) via Interactive Response Technology to receive subcutaneous secukinumab 150 mg with a loading dose (150 mg loading dose [LD] group), 150 mg without a loading dose (150 mg non–loading dose [NL] group), or placebo at baseline and weeks 1, 2, and 3, followed by every 4 weeks starting at week 4, The 150 mg NL group received placebo at weeks 1, 2, and 3 to maintain blinding. Study treatment was self-administered throughout the study using syringes prefilled with 150 mg/1 ml secukinumab or 1 ml placebo. Switch to open-label subcutaneous secukinumab 150 mg or standard of care was permitted after week 20 for inadequate responders based on clinical judgment of disease activity by the investigator and the patient.6
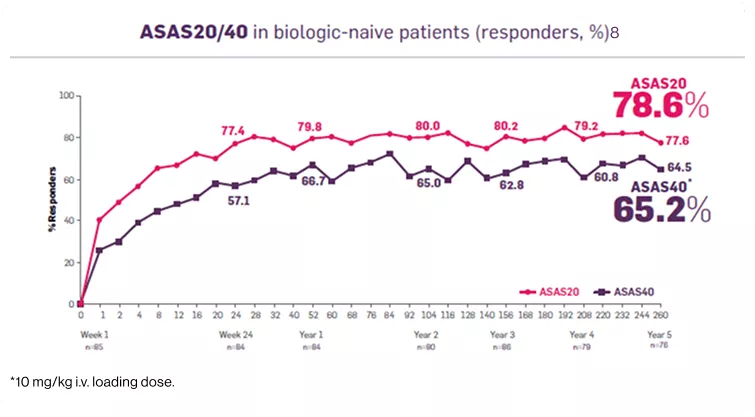
Cosentyx significantly reduced the signs and symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis.8 |
Additional data from the Measure 1 study:
As observed data in patients originally randomized to Cosentyx 150 mg without placebo switchers or patients whose dose was escalated.7
Significantly more patients achieved ASAS40 vs placebo at 1 week in 150-mg group (P<0.001; n=125, all population, 74% of whom were biologic-naive).8
Measure 1 study design
Objective: To present long-term (5 years), end-of-study efficacy and safety results for secukinumab from the MEASURE 1 trial in patients with AS, including results for patients whose dose was escalated from secukinumab 75 to 150 mg during the study.6
Study design: MEASURE 1 is a phase III, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled 2-year study, with 3-year extension , 371 Patients were initially randomised to receive either intravenous secukinumab 10 mg/kg at baseline, week 2 and week 4, followed by subcutaneous secukinumab 150 mg (intravenous → 150 mg) or 75 mg (intra-venous → 75 mg) every 4 weeks thereafter. Matched placebo was given on the same intravenous to subcutaneous dosing schedule. Placebo patients were re-randomised to secukinumab 150 mg subcutaneous or secukinumab 75 mg subcutaneous (placebo switchers) by week 16 (non-responders) or week 24 (responders).6
Elevated CRP may be a marker for the evolution of nonradiographic axial SpA to AS.
Interestingly, three cytokines strongly correlated with CRP elevations are interleukins (IL)-6,
IL-1, and IL-17.9
Significant improvement in the objective signs of inflammation in tumor necrosis factor inhibitor naive nr-axSpA patients.9
Improvement in MRI SI joint edema score at week 169

Patients who remained syndesmophyte-free at week 104.10
Patients who remained syndesmophyte-free at week 104 (%)10

†10 mg/kg i.v. loading dose.11

The primary goal of treating the patient with axSpA is to maximise long-term healthrelated quality of life through control of symptoms and inflammation, prevention of progressive structural damage.11 |
Additional data from the Measure 1 study:
Data presented are as observed.11
*No radiographic progression (mSASSS change from baseline <2) was observed over 208 week.11
*Syndesmophytes were considered present if mSASSS was ≥2 per specific affected vertebral unit.
Patients randomized to secukinumab received a 10 mg/kg intravenous loading dose at baseline and weeks 2 and 4, before receiving indicated dose of secukinumab subcutaneously every 4 weeks from week 8.10
Patients randomized to placebo were switched to receive indicated dose of subcutaneously every 4 weeks from week 16 or 24, depending upon clinical response.10
A large proportion of patients (>80%) had no spinal radiographic progression at week 104.10
Cumulative probability plot for change from base-line in the mSASSS through week 208.13

The primary goal of treating the patient with axSpA is to maximise long-term health-related quality of life through control of symptoms and inflammation, prevention of progressive structural damage.11 |
Additional data from the Measure 1 study:
Data represent New syndesmophyte formation through week 104 in x-ray completer cohort.10
*Syndesmophytes were considered present if mSASSS was ≥2 per specific affected vertebral unit.
Patients randomized to secukinumab received a 10 mg/kg intravenous loading dose at baseline and weeks 2 and 4, before receiving indicated dose of secukinumab subcutaneously every 4 weeks from week 8.10
Patients randomized to placebo were switched to receive indicated dose of subcutaneously every 4 weeks from week 16 or 24, depending upon clinical response.10
How would reducing disease activity help your patients get through the day?
Image
| Image
| Image
|
Nr-axsPA PATIENTS
Nr-axsPA 50% decrease in BASDAI | 27.3% of AS patients achieved | 30 patients with ASDAS-CRP |
BASDAI criteria for 50% improvement response in each treatment group through week 16.6 | ||
* 55.7% at week 52, 50.4% at week 104, 54.8% at week 156, 59% at week 208, 63.4% at week 260.
Cosentyx API
Cosentyx API
Footnotes:
AS=ankylosing spondylitis; axSpA=axial spondyloarthritis; ASAS: Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society criteria; nr-axSpA: non-radiographic axial SpondyloArthritis; s.c.: subcutaneous; i.v.=intravenous; MRI SI = Sacroiliac joint edema score on magnetic resonance imaging; LD = Loading Dose group; mSASSS=modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spinal Score; BASDAI=Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index.
References
Egyptian Drug Authority (EDA) Cosentyx 150,300 mg leaflet approval date: 23/03/2025.
MayoClinic. Evaluation and Management of the Patient With Suspected Inflammatory Spine Disease. Available at :https://www.mayoclinicproceedings.org/article/S0025-
6196(16)30826-6/fulltext#:~:text=Axial%20spondyloarthritis%20(AxSpA)%20is%20a,ends%20of%20the%20AxSpA%20spectrum. Last Accessed:07/03/2023.Ward MM. Health-related quality of life in ankylosing spondylitis: a survey of 175 patients. Arthritis care & research. 1999 Aug;12(4):247-55.
Druce KL, Aikman L, Dilleen M, Burden A, Szczypa P, Basu N. Fatigue independently predicts different work disability dimensions in etanercept-treated rheumatoid arthritis and
ankylosing spondylitis patients. Arthritis research & therapy. 2018 Dec;20(1):1-9.Rudwaleit M, Metter A, Listing J, Sieper J, Braun J. Inflammatory back pain in ankylosing spondylitis: a reassessment of the clinical history for application as classification and
diagnostic criteria. Arthritis & Rheumatism: Official Journal of the American College of Rheumatology. 2006 Feb;54(2):569-78.Deodhar A, Blanco R, Dokoupilova E, Hall S, Kameda H, Kivitz AJ, Poddubnyy D, van de Sande M, Wiksten AS, Porter BO, Richards HB. Improvement of signs and symptoms of nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis in patients treated with secukinumab: primary results of a randomized, placebo-controlled phase III study. Arthritis & Rheumatology. 2021 Jan;73(1):110-20.
Baraliakos X, Kivitz AJ, Deodhar AA, Braun J, Wei JC, Delicha EM, Talloczy Z, Porter B. Long-term effects of interleukin-17A inhibition with secukinumab in active ankylosing spondylitis: 3-year efficacy and safety results from an extension of the Phase 3 MEASURE 1 trial. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018 Jan 1;36(1):50-5.
Baeten D, Sieper J, Braun J, Baraliakos X, Dougados M, Emery P, Deodhar A, Porter B, Martin R, Andersson M, Mpofu S. Secukinumab, an interleukin-17A inhibitor, in ankylosing spondylitis. New England journal of medicine. 2015 Dec 24;373(26):2534-48.
Colbert RA. Early axial spondyloarthritis. Current opinion in rheumatology. 2010;22(5):603-7.
Braun J, Baraliakos X, Deodhar A, Baeten D, Sieper J, Emery P, Readie A, Martin R, Mpofu S, Richards HB. Effect of secukinumab on clinical and radiographic outcomes in ankylosing spondylitis: 2-year results from the randomised phase III MEASURE 1 study. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2017 Jun 1;76(6):1070-7. Available at :https://ard. bmj.com/content/76/6/1070, Last Accessed:04/06/2023.
Poddubnyy D, Haibel H, Listing J, Marker-Hermann E, Zeidler H, Braun J, Sieper J, Rudwaleit M. Baseline radiographic damage, elevated acute-phase reactant levels, and cigarette smoking status predict spinal radiographic progression in early axial spondylarthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 2012 May;64(5):1388-98.
Deodhar AA. Understanding axial spondyloarthritis: a primer for managed care. Am J Manag Care. 2019 Nov 1;25:319-0.
Braun J, Baraliakos X, Deodhar A, Poddubnyy D, Emery P, Delicha EM, Talloczy Z, Porter B. Secukinumab shows sustained efficacy and low structural progression in ankylosing spondylitis: 4-year results from the MEASURE 1 study. Rheumatology. 2019 May 1;58(5):859-68.
Approved by Egyptian Drug Authority:BF0424OA4792/092025. Invalidation date: 06/12/2026.
Kindly report any violated online promotional, educational and awareness material not having this message to The General administration for Regulation of Marketing & Advertising Materials at:
www.edaegypt.gov.eg
Image

|
BF0424OA4792/092025 |
Adverse Events Reporting We encourage using the following Electronic reporting tool for reporting into the safety database directly: |
