Kimlerde kullanılır?
İnklisiran, şu anda primer hiperkolesterolemisi olan (heterozigot ailesel ve ailesel olmayan) veya karma dislipidemisi olan yetişkinlerde diyete ek olarak aşağıdaki şekilde endikedir:
- tolere edilen maksimum statin dozu ile LDL-K hedeflerine ulaşamayan hastalarda bir statin veya statin ile diğer lipid düşürücü tedavilerle kombinasyon halinde ya da,
- tek başına veya diğer lipid düşürücü tedavilerle kombinasyonda statin intoleransı olan veya statinin kontrendike olduğu hastalarda
Nasıl kullanılır?
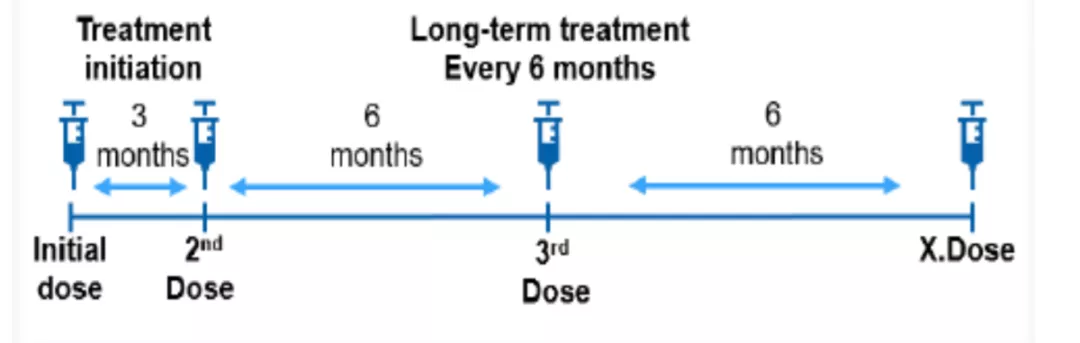
Önerilen doz; başlangıçta, 3. ayda ve ardından her 6 ayda bir, tek bir subkutan enjeksiyon olarak uygulanır.
Image
Referanslar:
- Wright RS, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023;82(24):2251–2261.
- European Heart Network. European cardiovascular disease statistics 2017 edition. http://www.ehnheart.org/cvd-statistics/cvd-statistics-2017.html
- Mensah GA, Roth GA, Fuster V. The Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors: 2020 and Beyond. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74(20):2529-2532, 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.10.009, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31727292
- World Health Organization. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds)
- World Health Organization. About cardiovascular diseases. https://www.who.int/cardiovascular_diseases/about_cvd/en/
- Herrington W, Lacey B, Sherliker P, Armitage J, Lewington S. Epidemiology of Atherosclerosis and the Potential to Reduce the Global Burden of Atherothrombotic Disease. Circ Res. 2016;118(4):535-546, 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.307611, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26892956
- Mach F, Baigent C, Catapano AL, et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J. 2020;41(1):111-188, 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz455
- Cannon CP, Khan I, Klimchak AC, Reynolds MR, Sanchez RJ, Sasiela WJ. Simulation of Lipid-Lowering Therapy Intensification in a Population With Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. JAMA Cardiol. 2017;2(9):959-966, 10.1001/jamacardio.2017.2289, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28768335
- Wong ND, Young D, Zhao Y, et al. Prevalence of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association statin eligibility groups, statin use, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol control in US adults using the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011-2012. J Clin Lipidol. 2016;10(5):1109-1118, 10.1016/j.jacl.2016.06.011, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27678427
- Fox KM, Tai MH, Kostev K, Hatz M, Qian Y, Laufs U. Treatment patterns and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) goal attainment among patients receiving high- or moderate-intensity statins. Clin Res Cardiol. 2018;107(5):380-388, 10.1007/s00392-017-1193-z, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29273856
- Allahyari A, Jernberg T, Lautsch D, et al. LDL-cholesterol target attainment according to the 2011 and 2016 ESC/EAS dyslipidaemia guidelines in patients with a recent myocardial infarction - nationwide cohort study, 2013-2017. Eur Heart J Qual Care Clin Outcomes. 2020, 10.1093/ehjqcco/qcaa016, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32142112
- Allen JM, Arnold SV, Lohr NL et al. Assessing low density lipoprotein cholesterol risk in secondary prevention patients within the PINNACLE National Outpatient Registry [abstract 12904]. Circulation. 2019;140:A12904. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/abs/10.1161/circ.140.suppl_1.12904?af=R
- Hermans MP, Castro Cabezas M, Strandberg T, et al. Centralized Pan-European survey on the under-treatment of hypercholesterolaemia (CEPHEUS): overall findings from eight countries. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010;26(2):445-454, 10.1185/03007990903500565, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20001658
- Park JE, Chiang CE, Munawar M, et al. Lipid-lowering treatment in hypercholesterolaemic patients: the CEPHEUS Pan-Asian survey. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2012;19(4):781-794, 10.1177/1741826710397100, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21450606
- Colantonio LD, Rosenson RS, Deng L, et al. Adherence to Statin Therapy Among US Adults Between 2007 and 2014. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019;8(1):e010376, 10.1161/JAHA.118.010376, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30616455
- Khvorova A. Oligonucleotide Therapeutics - A New Class of Cholesterol-Lowering Drugs. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(1):4-7, 10.1056/NEJMp1614154, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28052224
- Fitzgerald K, White S, Borodovsky A, et al. A Highly Durable RNAi Therapeutic Inhibitor of PCSK9. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(1):41-51, 10.1056/NEJMoa1609243, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27959715
- Goldstein JL, Brown MS. A century of cholesterol and coronaries: from plaques to genes to statins. Cell. 2015;161(1):161-172, 10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.036, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25815993
- Wicinski M, Zak J, Malinowski B, Popek G, Grzesk G. PCSK9 signaling pathways and their potential importance in clinical practice. EPMA J. 2017;8(4):391-402, 10.1007/s13167-017-0106-6, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29209441
- Fitzgerald K, Frank-Kamenetsky M, Shulga-Morskaya S, et al. Effect of an RNA interference drug on the synthesis of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) and the concentration of serum LDL cholesterol in healthy volunteers: a randomised, single-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 trial. Lancet. 2014;383(9911):60-68, 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61914-5, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24094767
- DeWeerdt S. RNA therapies explained. Treatments that target RNA or deliver it to cells fall into three broad categories, with hybrid approaches also emerging. Nature. 2019;574:52-53. https://media.nature.com/original/magazine-assets/d41586-019-03068-4/d41586-019-03068-4.pdf
- Kosmas CE, Munoz Estrella A, Sourlas A, et al. Inclisiran: A New Promising Agent in the Management of Hypercholesterolemia. Diseases. 2018;6(3), 10.3390/diseases6030063, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30011788
- Pharmacy Times. Murphy J (ed). Study: Durable, Potent LDL-C Reduction With Inclisiran for Cholesterol-Lowering. https://www.pharmacytimes.com/ajax/study-durable-potent-ldl-c-reduction-with-inclisiran-for-cholesterol-lowering
- Tsouka AN, Tellis CC, Tselepis AD. Pharmacology of PCSK9 Inhibitors: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(31):3622-3633, 10.2174/1381612824666181010144823, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30317986
- Rand TA, Petersen S, Du F, Wang X. Argonaute2 cleaves the anti-guide strand of siRNA during RISC activation. Cell. 2005;123(4):621-629, 10.1016/j.cell.2005.10.020, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16271385
- Steinberg D, Witztum JL. Inhibition of PCSK9: a powerful weapon for achieving ideal LDL cholesterol levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(24):9546-9547, 10.1073/pnas.0904560106, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19506257
- Wright, R.S. et al. Safety and Tolerability of Inclisiran for Treatment of Hypercholesterolemia in 7 Clinical Trials J Am Coll Cardiol 2023;82:2251–2261
- Lyptimzia Kısa Ürün Bilgisi (Onay tarihi 02.08.2024)
- LEQVIO. Core Data Sheet. Novartis Pharma AG; 2023
- Khvorova A. Oligonucleotide therapeutics – a new class of cholesterol-lowering drugs. N. Engl J Med. 2017;376(1):4-7. Doi:10.1056/NEJMp1614154
- Fitzgerald K, White S, Borodovsky A, et al. A highly durable RNAi therapeutic inhibitor of PCSK9. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(1):41-51. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1609243

