Yüksek kardiyovasküler (KV) riske sahip hastalarda inklisiran ile tamamlanmış ve devam eden 7 klinik çalışmadan elde edilen havuzlanmış post hoc analizde inklisirana uzun süreli maruziyetin, güvenlilik olaylarında artan bir insidansa yol açmadığı bulunmuştur.
Bu analiz aynı zamanda yüksek LDL-K seviyelerine sahip hastalarda, ASKVH, ASKVH risk eşdeğeri ve heterozigot ailesel hiperkolesterolemi ile birlikte, az sayıda homozigot ailesel hiperkolesterolemi hastalarında statinler ve/veya diğer oral lipid düşürücü tedaviler ile kombinasyon halinde yılda iki kez uygulanan inklisiran tedavisinin iyi tolere edildiğini gösteren en büyük veri setini sunmaktadır.
Sonuç olarak inklisiranın etkili ve tutarlı LDL-K düşürücü etkisi ile birlikte ele alındığında, veriler yüksek KV riski taşıyan hastalarda uzun süreli kullanımı için destek sağlamaktadır.
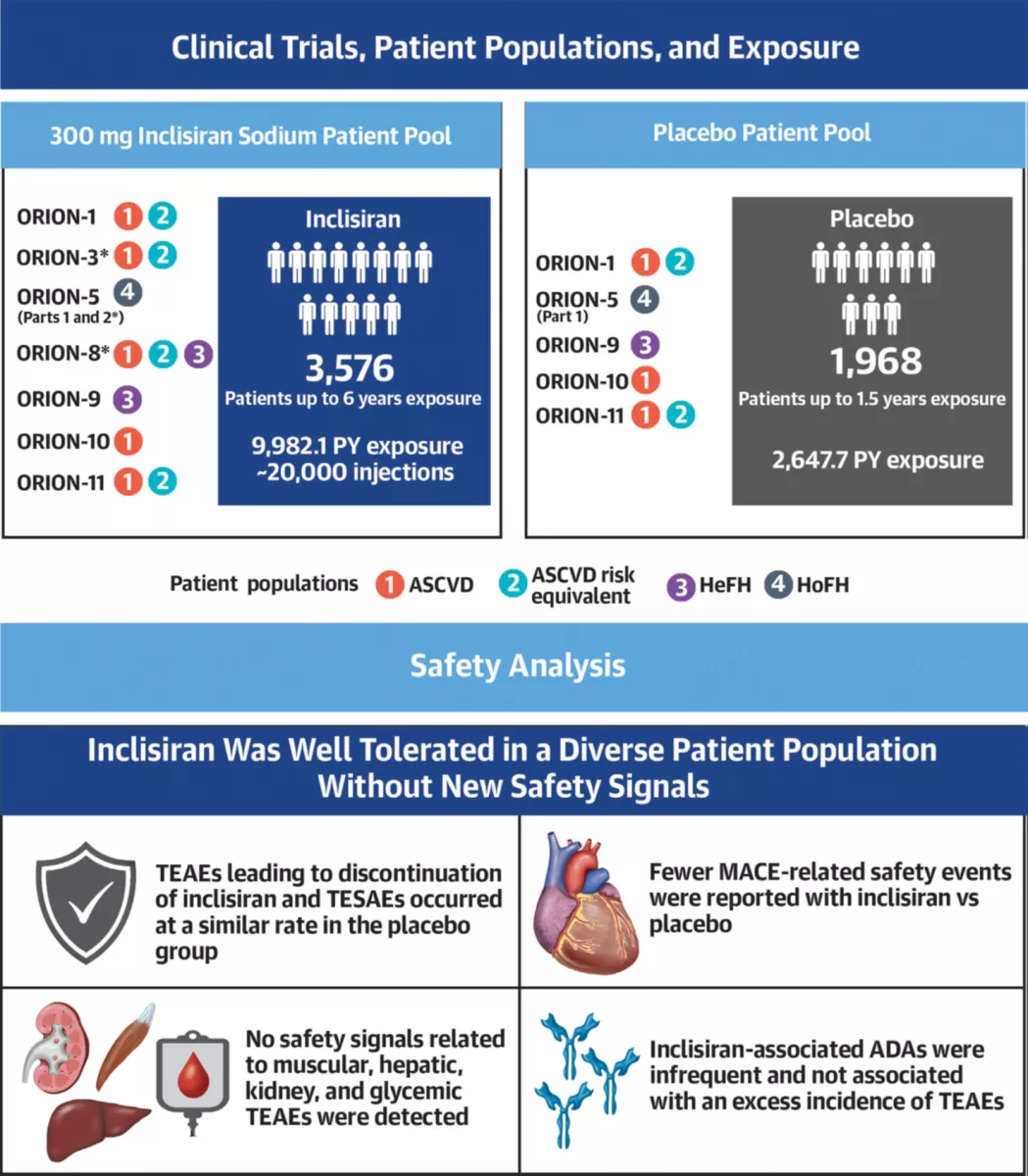
*Open-label extension trials.
ADA= antidrug antibody; ASCVD= atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; HeFH = heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia; HoFH = homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia; MACE = major adverse cardiovascular event; PY = patient-years; TEAE = treatmentemergent adverse event; TESAE = treatment-emergent serious adverse event.
Referanslar:
- Wright RS, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023;82(24):2251–2261.
- European Heart Network. European cardiovascular disease statistics 2017 edition. http://www.ehnheart.org/cvd-statistics/cvd-statistics-2017.html
- Mensah GA, Roth GA, Fuster V. The Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors: 2020 and Beyond. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74(20):2529-2532, 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.10.009, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31727292
- World Health Organization. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds)
- World Health Organization. About cardiovascular diseases. https://www.who.int/cardiovascular_diseases/about_cvd/en/
- Herrington W, Lacey B, Sherliker P, Armitage J, Lewington S. Epidemiology of Atherosclerosis and the Potential to Reduce the Global Burden of Atherothrombotic Disease. Circ Res. 2016;118(4):535-546, 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.307611, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26892956
- Mach F, Baigent C, Catapano AL, et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J. 2020;41(1):111-188, 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz455
- Cannon CP, Khan I, Klimchak AC, Reynolds MR, Sanchez RJ, Sasiela WJ. Simulation of Lipid-Lowering Therapy Intensification in a Population With Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. JAMA Cardiol. 2017;2(9):959-966, 10.1001/jamacardio.2017.2289, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28768335
- Wong ND, Young D, Zhao Y, et al. Prevalence of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association statin eligibility groups, statin use, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol control in US adults using the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011-2012. J Clin Lipidol. 2016;10(5):1109-1118, 10.1016/j.jacl.2016.06.011, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27678427
- Fox KM, Tai MH, Kostev K, Hatz M, Qian Y, Laufs U. Treatment patterns and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) goal attainment among patients receiving high- or moderate-intensity statins. Clin Res Cardiol. 2018;107(5):380-388, 10.1007/s00392-017-1193-z, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29273856
- Allahyari A, Jernberg T, Lautsch D, et al. LDL-cholesterol target attainment according to the 2011 and 2016 ESC/EAS dyslipidaemia guidelines in patients with a recent myocardial infarction - nationwide cohort study, 2013-2017. Eur Heart J Qual Care Clin Outcomes. 2020, 10.1093/ehjqcco/qcaa016, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32142112
- Allen JM, Arnold SV, Lohr NL et al. Assessing low density lipoprotein cholesterol risk in secondary prevention patients within the PINNACLE National Outpatient Registry [abstract 12904]. Circulation. 2019;140:A12904. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/abs/10.1161/circ.140.suppl_1.12904?af=R
- Hermans MP, Castro Cabezas M, Strandberg T, et al. Centralized Pan-European survey on the under-treatment of hypercholesterolaemia (CEPHEUS): overall findings from eight countries. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010;26(2):445-454, 10.1185/03007990903500565, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20001658
- Park JE, Chiang CE, Munawar M, et al. Lipid-lowering treatment in hypercholesterolaemic patients: the CEPHEUS Pan-Asian survey. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2012;19(4):781-794, 10.1177/1741826710397100, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21450606
- Colantonio LD, Rosenson RS, Deng L, et al. Adherence to Statin Therapy Among US Adults Between 2007 and 2014. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019;8(1):e010376, 10.1161/JAHA.118.010376, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30616455
- Khvorova A. Oligonucleotide Therapeutics - A New Class of Cholesterol-Lowering Drugs. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(1):4-7, 10.1056/NEJMp1614154, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28052224
- Fitzgerald K, White S, Borodovsky A, et al. A Highly Durable RNAi Therapeutic Inhibitor of PCSK9. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(1):41-51, 10.1056/NEJMoa1609243, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27959715
- Goldstein JL, Brown MS. A century of cholesterol and coronaries: from plaques to genes to statins. Cell. 2015;161(1):161-172, 10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.036, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25815993
- Wicinski M, Zak J, Malinowski B, Popek G, Grzesk G. PCSK9 signaling pathways and their potential importance in clinical practice. EPMA J. 2017;8(4):391-402, 10.1007/s13167-017-0106-6, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29209441
- Fitzgerald K, Frank-Kamenetsky M, Shulga-Morskaya S, et al. Effect of an RNA interference drug on the synthesis of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) and the concentration of serum LDL cholesterol in healthy volunteers: a randomised, single-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 trial. Lancet. 2014;383(9911):60-68, 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61914-5, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24094767
- DeWeerdt S. RNA therapies explained. Treatments that target RNA or deliver it to cells fall into three broad categories, with hybrid approaches also emerging. Nature. 2019;574:52-53. https://media.nature.com/original/magazine-assets/d41586-019-03068-4/d41586-019-03068-4.pdf
- Kosmas CE, Munoz Estrella A, Sourlas A, et al. Inclisiran: A New Promising Agent in the Management of Hypercholesterolemia. Diseases. 2018;6(3), 10.3390/diseases6030063, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30011788
- Pharmacy Times. Murphy J (ed). Study: Durable, Potent LDL-C Reduction With Inclisiran for Cholesterol-Lowering. https://www.pharmacytimes.com/ajax/study-durable-potent-ldl-c-reduction-with-inclisiran-for-cholesterol-lowering
- Tsouka AN, Tellis CC, Tselepis AD. Pharmacology of PCSK9 Inhibitors: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(31):3622-3633, 10.2174/1381612824666181010144823, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30317986
- Rand TA, Petersen S, Du F, Wang X. Argonaute2 cleaves the anti-guide strand of siRNA during RISC activation. Cell. 2005;123(4):621-629, 10.1016/j.cell.2005.10.020, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16271385
- Steinberg D, Witztum JL. Inhibition of PCSK9: a powerful weapon for achieving ideal LDL cholesterol levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(24):9546-9547, 10.1073/pnas.0904560106, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19506257
- Wright, R.S. et al. Safety and Tolerability of Inclisiran for Treatment of Hypercholesterolemia in 7 Clinical Trials J Am Coll Cardiol 2023;82:2251–2261
- Lyptimzia Kısa Ürün Bilgisi (Onay tarihi 02.08.2024)
- LEQVIO. Core Data Sheet. Novartis Pharma AG; 2023
- Khvorova A. Oligonucleotide therapeutics – a new class of cholesterol-lowering drugs. N. Engl J Med. 2017;376(1):4-7. Doi:10.1056/NEJMp1614154
- Fitzgerald K, White S, Borodovsky A, et al. A highly durable RNAi therapeutic inhibitor of PCSK9. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(1):41-51. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1609243

