Ilaris® UAE BSS
Ilaris® UAE BSS
Drug Regulatory Affairs
ILARIS® (canakinumab)
150 mg/1 mL Solution for injection in a vial
National Succinct Statement (NSS)
Version 7.1
Effective date: 14-May-2024
Safety Label Change (SLC) N/A
Tracking number:
Document status: Final
Property of Novartis Confidential
May not be used, divulged, published or otherwise disclosed
without the consent of Novartis
ILARIS® 150 mg/mL solution for injection
Important note: Before prescribing, consult full prescribing information, including instructions for use: link to the reference country website:
EU: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en
Disclaimer: This link will contain the most updated product information approved by the reference country.
Presentation: Canakinumab. solution for injection in a vial. Each vial contains 150 mg of canakinumab.
Indications:
Periodic fever syndromes
Ilaris is indicated for the treatment of the following autoinflammatory periodic fever syndromes in adults, adolescents and children aged 2 years and older:
Cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes
Ilaris is indicated for the treatment of cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS) including:
Muckle-Wells syndrome (MWS),
Neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease (NOMID) / chronic infantile neurological, cutaneous, articular syndrome (CINCA),
Severe forms of familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome (FCAS) / familial cold urticaria (FCU) presenting with signs and symptoms beyond cold-induced urticarial skin rash.
Tumour necrosis factor receptor associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS)
Ilaris is indicated for the treatment of tumour necrosis factor (TNF) receptor associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS).
Hyperimmunoglobulin D syndrome (HIDS)/mevalonate kinase deficiency (MKD)
Ilaris is indicated for the treatment of hyperimmunoglobulin D syndrome (HIDS)/mevalonate kinase deficiency (MKD).
Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF)
Ilaris is indicated for the treatment of Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF). It is recommended that Ilaris be given in combination with colchicine, if appropriate.
Ilaris is also indicated for the treatment of:
Still’s disease
Ilaris is indicated for the treatment of active Still’s disease including adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD) and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (SJIA) in patients aged 2 years and older
who have responded inadequately to previous therapy with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and systemic corticosteroids. Ilaris can be given as monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate.
Gouty arthritis
Ilaris is indicated for the symptomatic treatment of adult patients with frequent gouty arthritis attacks (at least 3 attacks in the previous 12 months) in whom non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and colchicine are contraindicated, are not tolerated, or do not provide an adequate response, and in whom repeated courses of corticosteroids are not appropriate.
Dosage and administration:
For CAPS, TRAPS, HIDS/MKD, FMF and Still’s disease, the treatment is to be initiated and supervised by a specialist physician experienced in the diagnosis and treatment of the relevant indication.
For gouty arthritis, the physician needs to be experienced in the use of biologics and Ilaris is to be administered by a healthcare professional.
Posology
CAPS: Adults, adolescents and children aged 2 years and older
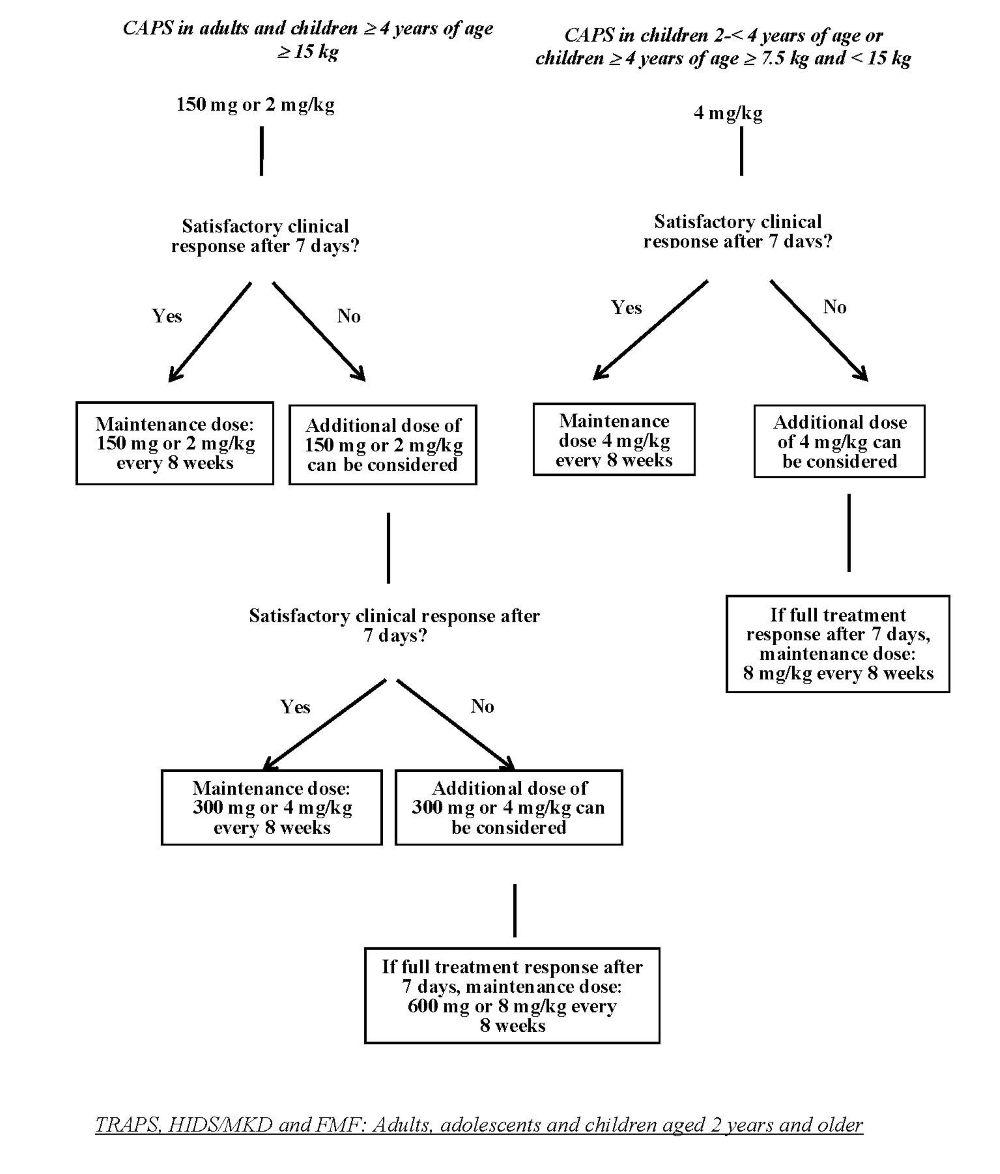
The recommended starting dose of canakinumab for CAPS patients is:
Adults, adolescents and children ≥ 4 years of age:
• 150 mg for patients with body weight > 40 kg
• 2 mg/kg for patients with body weight ≥ 15 kg and ≤ 40 kg
• 4 mg/kg for patients with body weight ≥ 7.5 kg and < 15 kg
Children 2 to < 4 years of age
• 4 mg/kg for patients with body weight ≥ 7.5 kg
This is administered every eight weeks as a single dose via subcutaneous injection.
For patients with a starting dose of 150 mg or 2 mg/kg, if a satisfactory clinical response (resolution of rash and other
generalised inflammatory symptoms) has not been achieved 7 days after treatment start, a second dose of canakinumab
at 150 mg or 2 mg/kg can be considered. If a full treatment response is subsequently achieved, the intensified dosing
regimen of 300 mg or 4 mg/kg every 8 weeks needs to be maintained. If a satisfactory clinical response has not been achieved
7 days after this increased dose, a third dose of canakinumab at 300 mg or 4 mg/kg can be considered. If a full treatment response
is subsequently achieved, maintaining the intensified dosing regimen of 600 mg or 8 mg/kg every 8 weeks is to be considered,
based on individual clinical judgement.
For patients with a starting dose of 4 mg/kg, if a satisfactory clinical response has not been achieved 7 days after treatment start,
a second dose of canakinumab 4 mg/kg can be considered. If a full treatment response is subsequently achieved, maintaining the
intensified dosing regimen of 8 mg/kg every 8 weeks is to be considered, based on individual clinical judgement.
Clinical experience with dosing at intervals of less than 4 weeks or at doses above 600 mg or 8 mg/kg is limited.
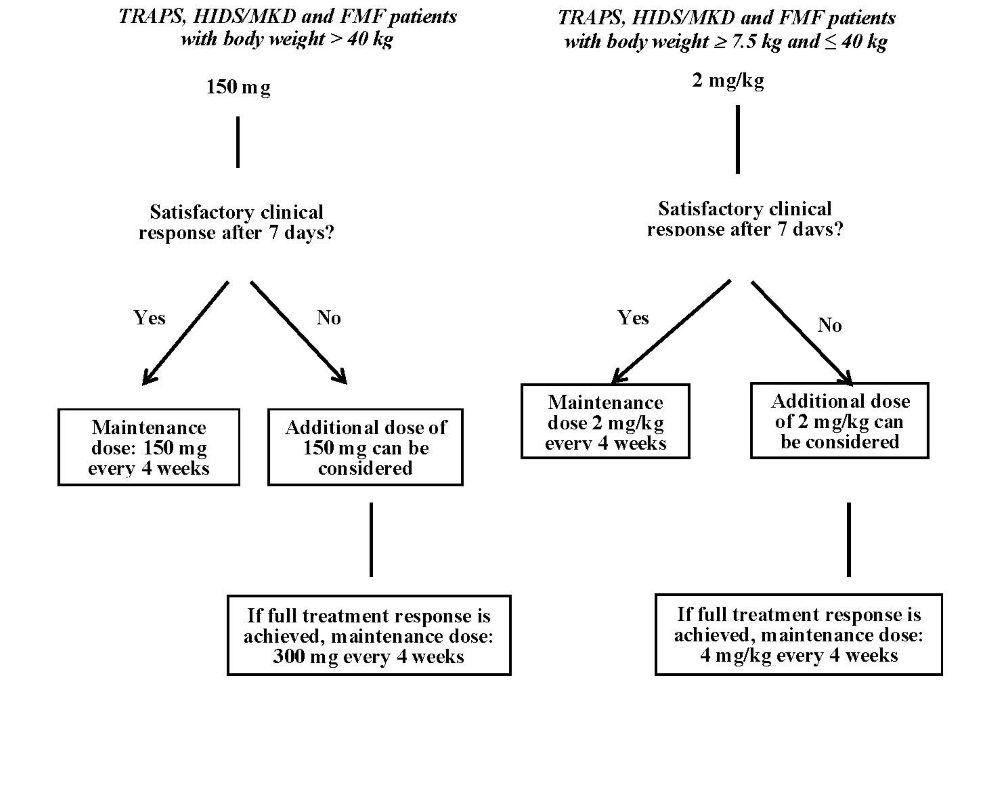
The recommended starting dose of canakinumab in TRAPS, HIDS/MKD and FMF patients is:
150 mg for patients with body weight > 40 kg
2 mg/kg for patients with body weight ≥ 7.5 kg and ≤ 40 kg
This is administered every four weeks as a single dose via subcutaneous injection.
If a satisfactory clinical response has not been achieved 7 days after treatment start, a second dose of canakinumab at 150 mg or 2 mg/kg can be considered. If a full treatment response is subsequently achieved, the intensified dosing regimen of 300 mg (or 4 mg/kg for patients weighing ≤ 40 kg) every 4 weeks needs to be maintained.
In patients without clinical improvement, it is recommended that the treating physician reconsiders continued treatment with canakinumab.
Still’s disease (SJIA and AOSD)
The recommended dose of canakinumab for patients with Still’s disease with body weight
≥ 7.5 kg is 4 mg/kg (up to a maximum of 300 mg) administered every four weeks via subcutaneous injection. In patients without clinical improvement, it is recommended that the treating physician reconsiders continued treatment with canakinumab.
Gouty arthritis
Management of hyperuricaemia with appropriate urate lowering therapy (ULT) needs to be instituted or optimised. Canakinumab needs to be used as an on-demand therapy to treat gouty arthritis attacks.
The recommended dose of canakinumab for adult patients with gouty arthritis is 150 mg administered subcutaneously as a single dose during an attack. For maximum effect, administration of canakinumab as soon as possible after the onset of a gouty arthritis attack is recommended.
It is recommended that patients who do not respond to initial treatment are not re-treated with canakinumab. In patients who respond and require re-treatment, there needs to be an interval of at least 12 weeks before a new dose of canakinumab may be administered (see section 5.2).
Missed doses
If an injection is missed in patients with CAPS, TRAPS, HIDS/MKD, FMF or Still’s disease (AOSD or SJIA), it is to be administered as soon as possible without waiting until the next scheduled dose. Subsequent doses are to be administered at the recommended intervals.
Special populations
Paediatric population
CAPS, TRAPS, HIDS/MKD and FMF
The safety and efficacy of canakinumab in CAPS, TRAPS, HIDS/MKD and FMF patients under 2 years of age have not been established. Currently available data are described in sections 4.8, 5.1 and 5.2 but no recommendation on a posology can be made.
SJIA
The safety and efficacy of canakinumab in SJIA patients under 2 years of age have not been established. No data are available.
Gouty arthritis
There is no relevant use of canakinumab in the paediatric population in the indication gouty arthritis.
Elderly
No dose adjustment is required.
Hepatic impairment
Canakinumab has not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment. No recommendation on a posology can be made.
Renal impairment
No dose adjustment is needed in patients with renal impairment. However, clinical experience in such patients is limited.
Patient Card
All prescribers of Ilaris shall be familiar with the SmPC and inform the patients/caregivers about the Patient Card explaining what to do should they experience any symptom of infection or macrophage activation syndrome (MAS), or in case of vaccinations prior to treatment. The physician will provide the Patient Card to each patient/caregiver.
Method of administration For subcutaneous use.
The following are suitable injection sites: upper thigh, abdomen, upper arm or buttocks. It is recommended to select a different injection site each time the product is injected to avoid soreness. Broken skin and areas which are bruised or covered by a rash
must be avoided. Injection into scar tissue must be avoided as this may result in insufficient exposure to canakinumab.
Vial
Each vial is for single use in a single patient, for a single dose.
CAPS, TRAPS, HIDS/MKD, FMF and Still’s disease (AOSD and SJIA)
After proper training in the correct injection technique, patients or their caregivers may inject canakinumab
if the physician determines that it is appropriate and with medical follow-up as necessary (see section 6.6).
Contraindications: Confirmed hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients. Active, severe infections.
Warnings and precautions: Infections: Associated with serious infections, exercise caution when administering to patients with infections, history of recurring infections, underlying conditions which may predispose them to infections. Treatment of gouty arthritis: should not be administered during an active infection. Treatment of CAPS, TRAPS, HIDS/MKD, FMF and Still’s disease (AOSD and SJIA): should not be initiated or continued
in patients with an active infection requiring medical intervention. Concomitant use with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors not recommended as may increase risk of serious infections. Opportunistic infections: May increase the risk of unusual or opportunistic infections. Tuberculosis: it is not known if the risk of reactivation of tuberculosis increases; before, during and after treatment patients should be monitored for active and latent tuberculosis infection. Due to potential false positive PPD skin test results, alternative means of screening for a tuberculosis infection should be considered for patients presenting with a positive PPD test while treated. Malignancy events: The risk of malignancies with anti- interleukin-1 therapy is unknown. Hypersensitivity: As with other injectable proteins, hypersensitivity reactions can occur, no anaphylactoid or anaphylactic reactions attributable to treatment with canakinumab were reported. Vaccinations: Should not be given concurrently with live vaccines. Neutropenia or leukopenia: Should not be initiated in patients with neutropenia or leukopenia. Assess neutrophil count prior to use. Macrophage activation syndrome (Still’s disease (AOSD and SJIA)): Macrophage activation syndrome (MAS) is a known, life-threatening disorder that may develop in patients with rheumatic conditions, in particular Still’s disease, and should be aggressively treated. Physicians should be attentive to symptoms of infection or worsening of Still’s disease, as these are known triggers for MAS. Based on the clinical trial experience, ILARIS does not appear to increase the incidence of MAS, but no definitive conclusion can be made. Hepatic function Transient and asymptomatic cases of elevations of serum transaminases or bilirubin have been reported in clinical trials Mutation in NLRP3 gene in CAPS patients Clinical experience in CAPS patients without a confirmed mutation in the NLRP3 gene is limited. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) has rarely been reported in patients treated with Ilaris, predominantly in patients with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA). Patients with DRESS may require hospitalization, as this condition may be fatal. If signs and symptoms of DRESS are present and an alternative aetiology cannot be established, Ilaris must not be re- administered and a different treatment considered This medicinal product contains 0.4 mg of polysorbate 80 in each 1 ml of solution for injection. Polysorbates may cause allergic reactions. The patient/caregiver needs to be instructed to tell the doctor if they or their child have/has any known allergies.
Pregnancy, lactation, females and males of reproductive potential: ILARIS should not be used in pregnant women unless clearly necessary. Administration of live vaccines to newborn infants exposed to canakinumab in utero is not recommended for 16 weeks following the mother's last dose of ILARIS before childbirth. ILARIS is not recommended during breast- feeding.
Adverse drug reactions:
Very common (≥10%): infections (e.g. nasopharyngitis, sinusitis, (viral) upper respiratory tract infection, pneumonia, rhinitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, bronchitis, ear infection, cellulitis, urinary tract infection, influenza, gastroenteritis, viral infection), abdominal pain
(upper), injection site reaction, decreased white blood cell counts, arthralgia, creatinine renal clearance decreased, proteinuria.
Common (≥1 to <10%): back pain, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue/asthenia, dizziness/vertigo, vaginal yeast infection, neutropenia.
Uncommon (≥0.1 to <1%): gastroesophageal reflux disease, platelet count decreased.
Adverse reaction from spontaneous report: opportunistic infections. Interactions: An increased incidence of serious infections has been associated with administration of another IL-1 blocker in combination with TNF inhibitors. Use of
canakinumab with TNF inhibitors is not recommended because this may increase the risk of
serious infections.
CYP450 substrates with a narrow therapeutic index: Upon initiation of ILARIS, therapeutic monitoring of the effect or of the active substance concentration should be performed and individual dose adjusted when needed.
No data are available on either the effects of live vaccination or the secondary transmission of infection by live vaccines in patients receiving canakinumab. Therefore, live vaccines must not be given concurrently with canakinumab unless the benefits clearly outweigh the risks. In case vaccination with live vaccines is indicated after initiation of canakinumab treatment, the recommendation is to wait for at least 3 months after the last canakinumab injection and before the next one.
Packs and prices: Country-specific.
Legal classification: Country-specific.
Leaflet revision date: February 2025.
NSS version number: 7.1
Leaflet presentation: R02.