

ILARIS® (canakinumab)
Indications1
Periodic fever syndromes
ILARIS is indicated for the treatment of the following autoinflammatory periodic fever syndromes in adults, adolescents and children aged 2 years and older:
Cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS), including:
Muckle-Wells syndrome (MWS)
Neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease (NOMID)/chronic infantile neurological, cutaneous, articular syndrome (CINCA)
Severe forms of familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome (FCAS)/familial cold urticaria (FCU) presenting with signs and symptoms beyond cold-induced urticarial skin rash
Tumour necrosis factor receptor associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS)
Hyperimmunoglobulin D syndrome (HIDS)/mevalonate kinase deficiency (MKD)
Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF)
ILARIS should be given in combination with colchicine, if appropriate
Still’s disease
ILARIS is indicated in patients who have responded inadequately to previous therapy with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and systemic corticosteroids, for the treatment of active Still’s disease, including:
Adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD)
Systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (SJIA) in patients aged 2 years and older
ILARIS can be given as monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate
Gouty arthritis
ILARIS is indicated for the symptomatic treatment of adult patients with frequent gouty arthritis attacks (at least 3 attacks in the previous 12 months) in whom non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and colchicine are contraindicated, are not tolerated, or do not provide an adequate response, and in whom repeated courses of corticosteroids are not appropriate.
What could ILARIS deliver to your patients?
ILARIS is the first selective IL-1β inhibitor for the treatment of FMF, HIDS/MKD, TRAPS, CAPS and Still’s disease (AOSD and SJIA) in adults, adolescents and children aged ≥2 years.1–3







ILARIS mechanism of action
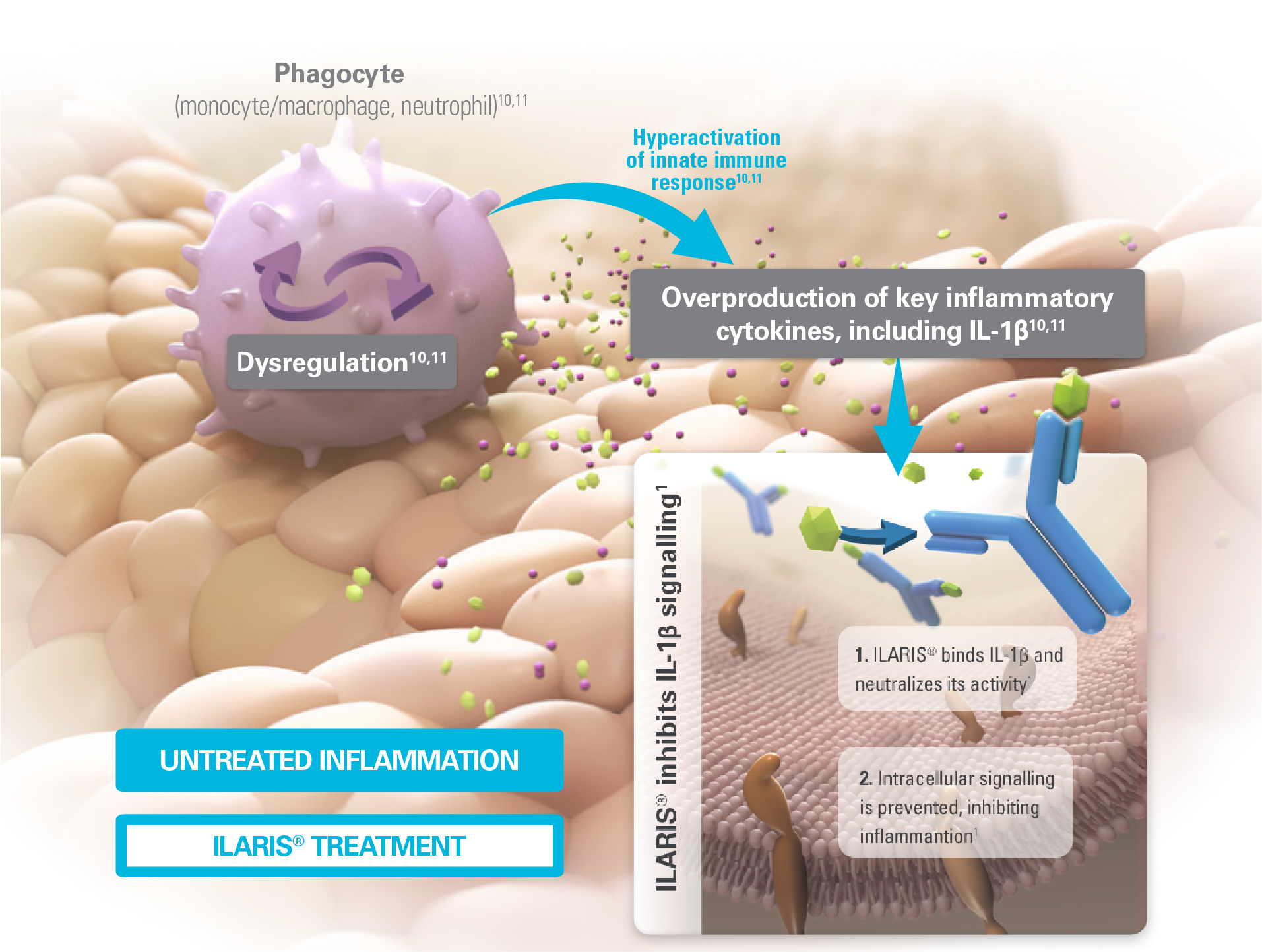
Image created using information from references 1, 10 and 11.
ILARIS works to help prevent IL-1β-induced gene activation and the production of inflammatory mediators1
Posology
CAPS
The recommended starting dose is (administered every eight weeks as a single dose via subcutaneous injection):
Adults, adolescents and children ≥4 years of age:
150 mg for patients with body weight >40 kg
2 mg/kg for patients with body weight ≥15 kg and ≤40 kg
4 mg/kg for patients with body weight ≥7.5 kg and <15 kg
Children 2 to <4 years of age:
4 mg/kg for patients with body weight ≥7.5 kg
TRAPS, HIDS/MKD and FMF
The recommended starting dose is (administered every four weeks as a single dose via subcutaneous injection):
150 mg for patients with body weight >40 kg
2 mg/kg for patients with body weight ≥7.5 kg and ≤40 kg
Still’s disease
The recommended dose of ILARIS for patients with Still’s disease with body weight ≥7.5 kg is 4 mg/kg (up to a maximum of 300 mg) administered every four weeks via subcutaneous injection.
For CAPS, TRAPS, HIDS/MKD, FMF and Still’s disease, the treatment should be initiated and supervised by a specialist physician experienced in the diagnosis and treatment of the relevant indication.
Gouty arthritis
The recommended starting dose of ILARIS for adult patients with gouty arthritis is:
150 mg administered subcutaneously as a single dose during an attack
For maximum effect, ILARIS should be administered as soon as possible after the onset of a gouty arthritis attack
For gouty arthritis, the physician should be experienced in the use of biologics and ILARIS should be administered by a healthcare professional.
Please refer to the SmPC for dose adjustments and the complete posology which includes information on the dosing if satisfactory clinical response has or has not been achieved after treatment start.
AOSD, adult-onset Still’s disease; CAPS, cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes; crFMF, colchicine-resistant familial Mediterranean fever; FCAS, familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome; FCU, familial cold urticaria; FMF, familial Mediterranean fever; HIDS, hyperimmunoglobulin D syndrome; IL, interleukin; JIA, juvenile idiopathic arthritis; MAS, macrophage activation syndrome; MKD, mevalonate kinase deficiency; NSAID, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; SC, subcutaneous; SJIA, systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis; TRAPS, tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome.
References
ILARIS® (canakinumab) Summary of Product Characteristics.
NHS England. Clinical Commissioning Policy: Canakinumab for treating periodic fever syndromes: TRAPS, HIDS/MKD and FMF (ages 2 years and older). February 2020. Available at: https://www.england.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/Canakinumab-for-tr... [Accessed May 2025].
NHS. Canakinumab engagement report. Available at: https://www.england.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/2002-canakinumab-e... [Accessed May 2025].
Özen S, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:1362–1369.
Migita K, et al. Immunologic Med 2018;41(2):55–61.
Karabulut Y, et al. Rheumatol Int 2022;42(1):81–86.
Tomaras S, et al. J Clin Med 2021;10(4):733.
Galozzi P, et al. Biologics 2021;16:21–34.
Efthimiou P, et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2021;51(4):858–874.
Lachmann HJ, et al. Arthritis Rheum 2011;63(2):314–324.
Lin YT et al. Autoimmun Rev 2011;10(8):482–489.
UK | May 2025 | FA-11307385
Adverse events should be reported. Reporting forms and information can be found at www.mhra.gov.uk/yellowcard. Adverse events should also be reported to Novartis online through the pharmacovigilance intake (PVI) tool at www.novartis.com/report, or alternatively email [email protected] or call 01276 698370.








